Unit 6. Heat, light and electricity

HEAT
Heat is the transfer of thermal energy.
It travels from the object with higher temperature to the object with the lower temperature.
Temperature is the amount of thermal energy in an object.How does heat transfer?
CONDUCTION: when two objects are in contact the heatis transferred from one object to the other.
CONVECTION: when heat travels through a gas or aliquid.
RADIATION: when the heat is transferred withoutcontact.
Materials
Conductors: transfer thermal energy easily. Example: metal.
Insulators: don´t transfer thermal energy. Example: wood
EFFECTS OF HEAT
There are 3 states of matter: solid, liquid and gas.
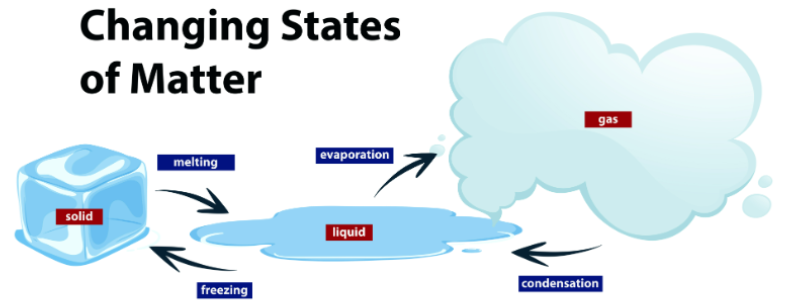 Melting: when a solid is heated, it turns into liquid.
Melting: when a solid is heated, it turns into liquid.
Evaporation: when a liquid is heated, it turns into gas.
Condensation: when a gas cools down, it turns into liquid.
Solidification: when a liquid cools down, it turns into solid.
Other changes:
Expansion: thermal energy causes the molecules to vibrate, as a result the material expands.
Chemical changes: thermal energy can make permanent changes in food.
LIGHT
Light is a form of radiant energy that we can see with our eyes and it is transferred through radiation.
It is made up of particles that travel in the form of electromagnetic waves.
Light travels in straight lines.
Object can react to light in different ways:
Transparent materials: does not block the light.
Translucent materials: block some light, but some light passes through the material.
Opaque materials: block the light.
There are:
Natural light sources: Sun Artificial light sources: light bulbs and screens
BASIC LAWS OF LIGHT
REFLECTION: occurs when light energy bounces off a surface and changes direction.
REFRACTION: occurs when light passes from one medium to another (water to air) and changes direction.
ELECTRICITY
Matter is made up of atoms.
Atoms have a nucleus.
The nucleus is made up of:
Protons that have a positive electric charge.
Neutrons that don´t have electric charge.
The electrons revolve around the nucleus and they have a negative electric charge.
NEUTRAL or CHARGED?
Electrically neutral: the same number of protons and electrons.
Electrically charged: different number of protons and electrons:
o Positively charged: there are more protons than electrons.
o Negatively charged: there are more electrons than protons.
Static electricity: is the accumulation of charged particles(positive or negative) in an object.
Objects that have opposite electric charges attract
Objects that have identical electric charges repel.
ELECTRIC CURRENT
Electric current is the movement of electrons between atoms.
Materials:
Electrical Conductors: electric current can flow easily.
Examples: metals, water…
Electrical Insulators: electric current can´t flow through them.
Examples: wood, plastic…
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
An electrical circuit is a group of elements that allow an electric current to Flow.
COMPONENTS OF A CIRCUIT:
Generators: transform different types of energy into electrical energy and produce an electrical current. Examples: batteries, alternators or solar panels.
Conducting cables: transport an electrical current from the generator to the receptor. They are usually covered in an insulating material.
Switches: are used to turn an electrical current on and off.
Receptors: use the electrical energy that has been transported to them by the cable. Examples: light bulbs, ovens…



